Final Exam
Section
4
(Answer all questions in this
section)
1.
The ______________ is the location
into which you will store and save your files.
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Perspective
Workspace (*)
Editor
None of the above
2.
Multiple windows are used when
more than one file is open in the edit area. True or False? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
3.
A workspace can have one or more
stored projects. True or false? Mark
for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False
4.
Tabs are used when more than one
file is open in the edit area. True or False?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False
5.
A _______________ is used to
organize Java related files. Mark for
Review
(1)
Points
Collection
Project
Package (*)
Workspace
Section
4
(Answer all questions in this
section)
6.
Which of the two diagrams below
illustrate the general form of a Java program?
Mark
for Review
(1)
Points
Example A
Example B (*)
7.
The following defines a package
keyword: Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Provides the compiler information
that identifies outside classes used within the current class.
Precedes the name of the class.
Defines where this class lives
relative to other classes, and provides a level of access control. (*)
8.
The following code is an example
of a correct initialization statement:
char
c="c"; Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
9.
Suppose that str1 and str2 are two
strings. Which of the statements or expressions are valid? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Str1 -= str2;
str1 >= str2
str1 += str2; (*)
String str3 = str1 - str2;
10.
Which of the following creates a
String named string? Mark for
Review
(1)
Points
String String;
String s;
String char;
char string;
String string; (*)
Section
4
(Answer all questions in this
section)
11.
Which of the following creates a
String reference named s and instantiates it?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
(Choose all
correct answers)
s="s";
String s;
String s=new String("s");
(*)
String s=""; (*)
12.
Which of the following creates a
String reference named str and instantiates it?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
str="str";
String str=new
String("str"); (*)
String str;
String s="str";
13.
Which line of code does not assign
3.5 to the variable x? Mark for
Review
(1)
Points
x=7.0/2.0;
x=3.5;
double x=3.5
3.5=x; (*)
14.
Which line of Java code assigns the
value of 5 raised to the power of 8 to a?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
int a=Math.pow(8,5);
double a=15^8;
double a=Math.pow(5,8); (*)
int a=Math.pow(5,8);
double a=pow(8,5);
15.
What two values can a boolean
variable have? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Integers and floating point types
Arithmetic and logic operators
True and false (*)
Relational and logic operators
Numbers and characters
Section
5
(Answer all questions in this
section)
16.
The following prints Yes on the
screen. True or false?
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
17.
How would you use the ternary
operator to rewrite this if statement?
if
(gender == "female") System.out.print("Ms.");
else
System.out.print("Mr."); Mark for Review
(1)
Points
System.out.print( (gender ==
"female") ? "Mr." : "Ms." );
(gender == "female") ?
"Ms." : "Mr." ;
System.out.print( (gender ==
"female") ? "Ms." : "Mr." ); (*)
(gender == "female") ?
"Mr." : "Ms." ;
18.
Which of the following expressions
will evaluate to true when x and y are boolean variables with opposite values?
I.
(x || y) && !(x && y)
II.
(x && !y) || (!x && y)
III.
(x || y) && (!x ||!y)
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
I only
II only
I and III
II and III
I, II, and III (*)
19.
Why are loops useful? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
They save programmers from having to
rewrite code.
They allow for repeating code a
variable number of times.
They allow for repeating code until
a certain argument is met.
All of the above. (*)
20.
A counter used in a for loop cannot
be initialized within the For loop header. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
Section
5
(Answer all questions in this
section)
21.
Which of the following best
describes a while loop? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
A loop that contains a counter in
parenthesis with the conditional statement.
A loop that executes the code at
least one time even if the conditional statement is false.
A loop that is executed repeatedly
until the conditional statement is false. (*)
A loop that contains a segment of
code that is executed before the conditional statement is tested.
Section 6
(Answer all questions in this
section)
22.
A logic error occurs if an unintentional
semicolon is placed at the end of a loop initiation because the interpreter
reads this as the only line inside the loop, a line that does nothing.
Everything that follows the semicolon is interpreted as code outside of the
loop. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
23.
What does it mean to catch an
exception? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
It means you have fixed the error.
It means there was never an
exception in your code.
It means to handle it. (*)
It means to throw it.
24.
What do exceptions indicate in Java? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
(Choose all
correct answers)
The code has considered and dealt
with all possible cases.
The code was not written to handle
all possible conditions. (*)
A mistake was made in your code. (*)
Exceptions do not indicate anything,
their only function is to be thrown.
There are no errors in your code.
25.
Which of the following would be a
correct way to handle an index out of bounds exception? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
(Choose all
correct answers)
Rewrite your code to avoid the
exception by not permititng the use of an index that is not inside the array.
(*)
Throw the exception that prints out
an error message. There is no need to have the catch handle the exception if it
has already been thrown.
Throw the exception and catch it. In
the catch, set the index to the index of the array closest to the one that was
out of bounds. (*)
Do nothing, it will fix itself.
Section
6
(Answer all questions in this
section)
26.
The following creates a reference in
memory named k that can refer to six different integers via an index. True or
false?
int
k[]= int[6]; Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
27.
What is the output of the following
segment of code?
int
num[]={9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
for(int
i=0;i<9 i="i+3)" o:p="">
System.out.print(num[i]); Mark for Review
(1)
Points
97531
987654321
9630
963 (*)
This code doesn't compile.
28.
What is the output of the following
segment of code?
int
array[][] = {{1,2,3},{3,2,1}};
for(int
i=0;i<2 i="" o:p="">
for(int
j=0;j<3 j="" o:p="">
System.out.print(2*array[1][1]); Mark for Review
(1)
Points
246642
444444 (*)
222222
This code doesn't compile.
123321
29.
What is the output of the following
segment of code?
Mark
for Review
(1)
Points
1286864
643432
666666 (*)
262423242322
This code does not compile.
Section
7
(Answer all questions in this
section)
30.
Which of the following could be a
reason to return an object? Mark
for Review
(1)
Points
Because you wish to be able to use
that object inside of the method.
It has faster performance than
returning a primitive type.
The method makes changes to the
object and you wish to continue to use the updated object outside of the
method. (*)
None of the above. It is not
possible to return an object.
Section
7
(Answer all questions in this
section)
31.
Which of the following is the
definition for a variable argument method?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
A way to create a new class.
A type of argument that enables
calling the same method with a different number of arguments. (*)
Having more than one constructor
with the same name but different arguments.
Specifies accessibility to code.
32.
You are assigned to write a method
that compares two objects of type Career. One requirement of your assignment is
to have your method compare the "greatestPossibleSalary" instance
data of Career objects. The "greatestPossibleSalary" field is data
type int.
What
would be the best return type from your compare method? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Array, because it can store the most
information.
Integer, because it is the easiest
to code with.
Career, because if it returns the
highest paying Career object it will be able to use the same method later to
compare other aspects of Career objects. (*)
String, because is should return a
string of the name of the career that is highest paying because none of the
other information of the career matters.
33.
What type(s) would work for a
variable argument method? Mark for
Review
(1)
Points
(Choose all
correct answers)
Integers, Strings, and Booleans (*)
Constructors
Arrays (*)
Objects (*)
All of the above
34.
Following good programming
guidelines, what access modifier should be used for the class fields in the
following situation?
A
car insurance company wants to create a class named Customer that stores all
data for a specified customer including the fields: vehicle information, policy
information, and a credit card number.
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
public
protected
private (*)
default
All of the above
35.
Methods are generally declared as
public so other classes may use them. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False
Section
7
(Answer all questions in this
section)
36.
Which of the following correctly
describes an "is-a" relationship?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
A helpful term used to conceptualize
the relationships among nodes or leaves in an inheritance hierarchy. (*)
A programming philosophy that
promotes simpler, more efficient coding by using exiting code for new
applications.
A programming philosophy that
promotes protecting data and hiding implementation in order to preserve the
integrity of data and methods.
It restricts access to a specified
segment of code.
37.
Which of the following demonstrates
the correct way to create an applet Battlefield? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
public class Applet extends
Battlefield{...}
public class
Battlefield(Applet){...}
public class Battlefield extends
Applet{...} (*)
public Applet Battlefield{...}
38.
What is encapsulation? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
A structure that categorizes and
organizes relationships among ideas, concepts of things with the most general
at the top and the most specific at the bottom.
A keyword that allows or restricts
access to data and methods.
A programming philosophy that
promotes simpler, more efficient coding by using exiting code for new
applications.
A programming philosophy that
promotes protecting data and hiding implementation in order to preserve the
integrity of data and methods. (*)
39.
The following code creates an object
of type Horse:
Whale
a=new Whale(); Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
40.
Which of the following keywords are
used to access the instance variables of an object from within the class code
for that object? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
private
protected
public
this (*)
Section
7
(Answer all questions in this
section)
41.
Which constructor code populates the
instance variables of the class correctly?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
42.
Which of the following calls the
method calculate correctly?
(1)
Points
ThisClass t=new ThisClass(); int
x=t.calculate(3);
ThisClass t=new ThisClass(); int
x=t.calculate(3,4); (*)
int x=calculate(3,4);
ThisClass t=new ThisClass(); int
x=t.calculate();
43.
Which of the following creates a
method that returns a boolean value?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
None of the above.
44.
A constructor must have the same
name as the class where it is declared. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False
45.
Which of the following is a goal of
the object model? Mark for
Review
(1)
Points
(Choose all
correct answers)
Concealing implementation. (*)
Providing modular code that can be
reused by other programs or classes. (*)
Protecting information and limiting
other classes' ability to change or corrupt data. (*)
Data abstraction. (*)
Section
7
(Answer all questions in this
section)
46.
Which of the following can be
declared final? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
Classes
Methods
Local variables
Method parameters
All of the above (*)
47.
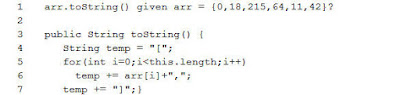
If we override the toString() method
with the code below, what would be the result of printing?
Mark for Review
(1)
Points
It would print the array backwards.
The console screen would display: 42 11 64 215 18 0
It would print the string returned
from the method. The console screen would display: {0, 18, 215, 64, 11, 42}
It would print the array one element
at a time. The console screen would display: 0 18 215 64 11 42
It would print the string returned
from the method. The console screen would display: [0,18,215,64,11,42,] (*)
48.
You can use an inner static class to
return an instance of its outer class container. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False
49.
You can return an instance of a
private class through a static method of a different class. True or false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True
False (*)
50.
You can assign new values to static
variables by prefacing them with the this keyword and a dot or period. True or
false? Mark for Review
(1)
Points
True (*)
False












I have to thank for sharing this blog, it is really helpful and I learned a lot.
BalasHapusPython for Data Engineering: Why Do Data Engineers Use Python?